Proper maintenance of your Cummins generator set is essential for ensuring reliable power generation when you need it most. Industrial facilities, hospitals, data centers, and commercial buildings depend on these robust power solutions to maintain critical operations during outages. Understanding the comprehensive maintenance requirements will help you maximize equipment lifespan, optimize performance, and prevent costly emergency repairs. A well-maintained generator set delivers consistent power output while minimizing operational costs and downtime risks.
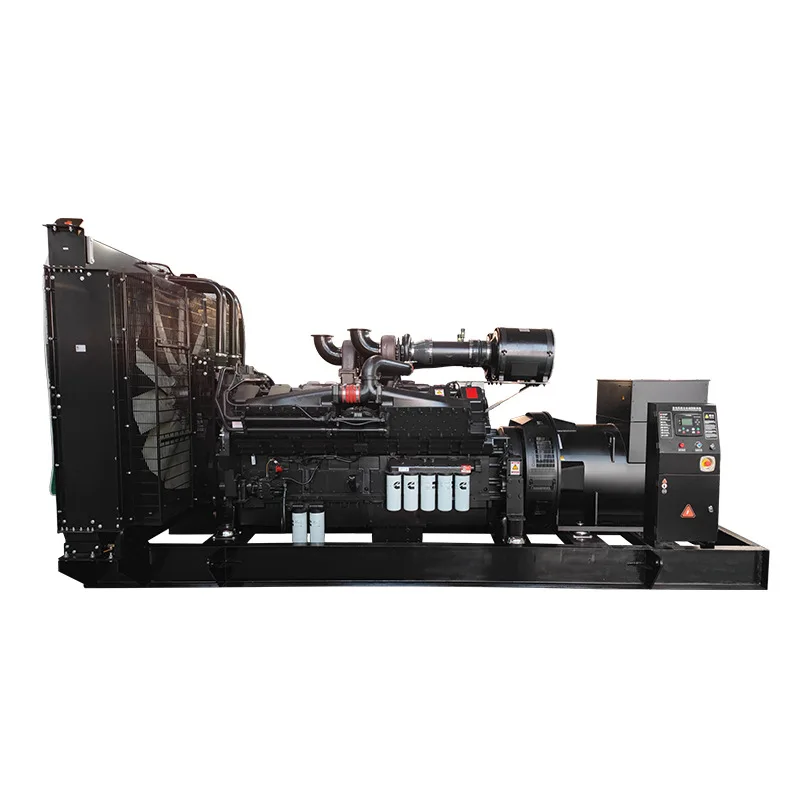
Modern generator sets require systematic maintenance approaches that address engine components, electrical systems, cooling mechanisms, and fuel delivery systems. Each component plays a critical role in overall system reliability and performance. Regular maintenance schedules help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems that could compromise your power security. Professional maintenance practices ensure your investment continues delivering value for decades.
Essential Maintenance Components and Systems
Engine Oil Management and Analysis
Engine oil serves as the lifeblood of your generator set, providing lubrication, cooling, and contamination removal functions. Regular oil changes using manufacturer-specified grades ensure optimal engine protection and performance. Oil analysis programs help identify internal wear patterns, contamination sources, and potential mechanical issues before they cause significant damage. Most industrial applications require oil changes every 250-500 operating hours, depending on load factors and environmental conditions.
Quality oil filters must be replaced during each oil change to maintain proper filtration efficiency. Bypass filtration systems can extend oil change intervals while providing superior contamination control. Monitor oil levels regularly and investigate any unusual consumption patterns that might indicate internal leakage or combustion issues. Proper oil management directly impacts engine longevity and operational reliability.
Cooling System Maintenance Protocols
The cooling system prevents engine overheating while maintaining optimal operating temperatures across varying load conditions. Coolant mixture ratios must meet manufacturer specifications to provide proper freeze protection, corrosion inhibition, and heat transfer properties. Radiator cleaning removes accumulated debris that restricts airflow and reduces cooling efficiency. Regular pressure testing identifies potential leaks before they cause catastrophic overheating events.
Water pump inspection ensures proper coolant circulation throughout the engine block and radiator assembly. Thermostat functionality verification confirms proper temperature regulation during startup and normal operation phases. Coolant replacement intervals typically range from 1000-3000 operating hours, depending on coolant type and operating conditions. Temperature monitoring systems provide early warning of potential cooling system problems.
Fuel System Optimization and Care
Fuel Quality Management Standards
Fuel quality significantly impacts engine performance, emissions compliance, and component longevity. Water contamination represents one of the most common fuel-related problems, promoting microbial growth and corrosion within fuel system components. Regular fuel testing identifies contamination levels, biological growth, and chemical degradation that could affect engine operation. Fuel polishing systems remove water and particulate contamination while restoring fuel quality to acceptable standards.
Fuel additives provide additional protection against degradation, biological growth, and cold weather issues. Biocide treatments eliminate microbial contamination that can clog filters and corrode fuel system components. Fuel rotation practices ensure stored fuel maintains acceptable quality levels over extended periods. Primary and secondary fuel filters require regular replacement based on differential pressure readings and maintenance schedules.
Injection System Maintenance Requirements
Modern diesel injection systems operate under extremely high pressures and tight tolerances that demand clean fuel and proper maintenance. Fuel injector cleaning or replacement ensures proper spray patterns and fuel atomization for optimal combustion efficiency. High-pressure fuel pumps require periodic inspection and calibration to maintain proper fuel delivery rates. Injection timing verification ensures optimal power output and emissions performance.
Electronic control modules monitor injection parameters and provide diagnostic information for troubleshooting performance issues. Regular software updates ensure compatibility with current emissions standards and performance optimization algorithms. Fuel system bleeding procedures remove air that could cause performance problems or starting difficulties. Professional injection system service typically occurs during major maintenance intervals or when performance issues arise.
Electrical System Inspection and Testing
Battery Maintenance and Testing Procedures
Starting batteries provide the electrical power necessary for engine cranking and initial system startup. Battery terminals require regular cleaning to prevent corrosion that could interrupt electrical connections during critical startup sequences. Electrolyte level monitoring ensures proper battery chemistry and prevents damage from low fluid conditions. Load testing verifies battery capacity under actual starting load conditions rather than simple voltage measurements.
Battery charger systems maintain proper charge levels during standby periods while preventing overcharging that could reduce battery life. Temperature compensation features adjust charging rates based on ambient conditions to optimize battery performance and longevity. Most industrial cummins generator set installations utilize multiple battery configurations for enhanced reliability and extended cranking capacity.
Alternator and Electrical Component Care
The alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical power while maintaining proper voltage and frequency regulation. Brush inspection and replacement ensure proper electrical contact and prevent damage to slip rings or commutator surfaces. Bearing lubrication maintains smooth operation and prevents premature failure of rotating components. Insulation testing verifies electrical integrity and identifies potential breakdown risks before they cause failures.
Control panel components require periodic inspection and calibration to ensure accurate monitoring and proper automatic operation. Digital controllers provide extensive diagnostic capabilities that help identify developing problems before they affect system performance. Wiring harness inspection identifies chafing, corrosion, or connection problems that could cause intermittent faults or complete system failures. Grounding system integrity verification prevents electrical safety hazards and ensures proper system operation.
Air System Maintenance Essentials
Air Filter Service and Replacement
Clean air intake prevents contamination from entering the combustion chambers where it could cause premature wear and performance degradation. Air filter elements require regular inspection and replacement based on restriction indicators or scheduled maintenance intervals. Pre-cleaner systems remove larger particles before they reach primary filter elements, extending filter life and improving filtration efficiency. Proper filter installation prevents bypass that could allow unfiltered air to enter the engine.
Turbocharger systems compress intake air to increase power density and fuel efficiency. Turbocharger inspection includes checking for oil leaks, unusual noise, or excessive play in rotating assemblies. Intercooler cleaning removes accumulated debris that restricts airflow and reduces cooling efficiency. Air intake system sealing prevents contamination bypass and ensures all intake air passes through filtration systems.
Exhaust System Maintenance Protocols
Exhaust systems remove combustion gases while meeting environmental emission standards and noise regulations. Exhaust manifold inspection identifies cracks or leaks that could affect engine performance or create safety hazards. Muffler and silencer maintenance ensures proper noise attenuation while preventing excessive backpressure that could reduce engine power output. Emission control systems require periodic service to maintain compliance with environmental regulations.
Exhaust temperature monitoring provides valuable diagnostic information about engine condition and combustion efficiency. High exhaust temperatures may indicate injection problems, air filter restrictions, or cooling system issues. Exhaust gas analysis helps verify proper combustion and emissions compliance during routine maintenance procedures. Professional exhaust system service addresses safety concerns and regulatory compliance requirements.
Preventive Maintenance Scheduling Strategies
Daily and Weekly Inspection Routines
Regular visual inspections identify developing problems before they cause equipment failures or safety hazards. Daily checks include fluid level verification, belt tension assessment, and general cleanliness maintenance. Weekly testing procedures verify automatic start capabilities, transfer switch operation, and alarm system functionality. Documentation of inspection results provides valuable trend information for predictive maintenance planning.
Exercise running maintains component lubrication, prevents fuel system problems, and verifies system readiness for emergency operation. Load bank testing confirms power output capabilities and identifies performance degradation trends. Fuel system cycling prevents fuel degradation and maintains injection system cleanliness. Regular exercise schedules typically include monthly loaded operation for 30-60 minutes under varying load conditions.
Annual Maintenance and Overhaul Planning
Comprehensive annual maintenance addresses components that require less frequent service while ensuring continued reliability and performance. Valve adjustment maintains proper engine timing and compression ratios for optimal power output and fuel efficiency. Timing chain or belt replacement prevents catastrophic engine damage from component failure. Major component inspections identify wear patterns that could require attention during the next maintenance cycle.
Professional maintenance documentation tracks component condition, replacement history, and performance trends that guide future service planning. Preventive replacement of wear items prevents unexpected failures during critical operation periods. Warranty compliance requires adherence to manufacturer maintenance schedules and use of approved parts and fluids. Annual maintenance planning coordinates service activities to minimize operational disruption while ensuring system reliability.
FAQ
How often should I change the oil in my generator set
Oil change intervals depend on several factors including operating hours, load conditions, and environmental factors. Most industrial applications require oil changes every 250-500 operating hours. Standby units with minimal runtime may extend intervals to 12-24 months based on calendar time. Oil analysis programs provide the most accurate guidance for optimizing change intervals based on actual oil condition rather than arbitrary schedules.
What are the signs that my generator needs immediate maintenance
Warning signs include unusual noise or vibration, excessive exhaust smoke, irregular engine operation, or failure to start reliably. Fluid leaks, overheating, or abnormal gauge readings also indicate immediate attention requirements. Electronic control systems typically provide diagnostic codes that identify specific problems requiring professional diagnosis. Any safety-related concerns such as fuel leaks or electrical problems require immediate shutdown and professional service.
Can I perform maintenance on my generator set myself
Basic maintenance tasks such as visual inspections, fluid level checks, and air filter replacement can typically be performed by qualified facility personnel. Complex procedures involving engine timing, injection systems, or electrical components require professional technicians with specialized training and equipment. Warranty requirements often mandate professional service for major maintenance procedures. Safety considerations and environmental regulations may also require professional service for certain maintenance activities.
How do I know if my generator set is properly sized for my facility
Proper sizing requires comprehensive load analysis including starting requirements, continuous loads, and future expansion needs. Professional load studies consider power factor, harmonic distortion, and voltage regulation requirements. Undersized units may not start large motors or maintain proper voltage under full load conditions. Oversized units operate inefficiently and may experience wet stacking problems in diesel engines. Regular load monitoring helps verify adequate sizing and identifies changing facility requirements.

