Lokacin da ayyukan kasuwanci suka sha’awa akan kama mai tsada abubuwa, Perkins generator set yana daya daga cikin ayyukan masu amintamma a sarayi. Wadannan kayan jari na diesel suna kirkirce su kaiwa ayyukan da za su yi ne a karkashin alamomin kasuwanci da ayyukan kasuwanci. Amma, kamar wani kayan inganci mai mahimmanci, a lokaci gudaɗawa suna buƙatar karɓar gudanarwa don kiyaye aiki mai zurfi. Fahimtar batutuwa masu damu da halayensu zai iya kare sababbin kasa da kuma kara shekarun aiki na kayan karewa.
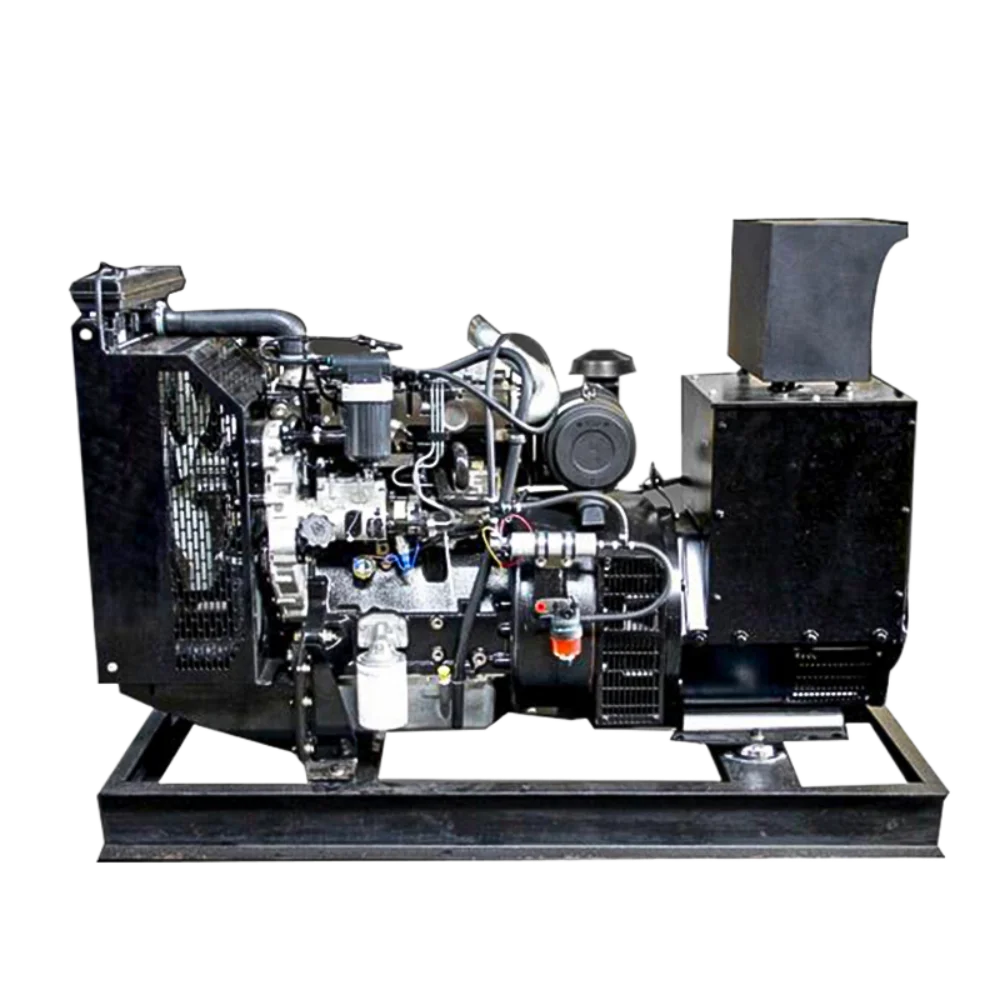
Ana buƙatar gyara-gyaran da ma'aikatan tallafawa don ƙare da kama-tsakanin yadda ake amfani da tsarin kuwar kudi. Wannan shirye-shiryen yadudduka yana bada irin batutuwan da ke fuskanta masu amfani kuma yana ba da hanyoyin gano da amincewa irin batutuwan da ke fuskanta. Ko kamar yadda kuke tafi da batutun sake fara, batutun aiki ko batutun kudin elektariku, fahimtar ilimin ilimi na ma'aikatan tallafawa zai bai ka iya gyara ainihin aiki zuwa inganci.
Batutun Farar Mesin da Batutun Aiki
Wasu Batutun Farar Da A Cikin Lahira
Kurudan kuskuren suna nuna wani daga cikin abubuwan da aka iya fuskantar da su a tsarin kugan kari na disel. Kusan kugan Perkins zai iya kuskure saboda dalilai mai yawa kamar masallaci na tsarin sadza, masallaci na batiri ko masallaci na ilimin ingginzafi. Gabatarwa gabata a matsayin karfafa kuskuren kuskure yana buƙatar duba tsarin sadza don tabbatar da tama’a na disel, kwaliti na sadza, da igiyoyin sadza masu farfaru. Sadza mara amfani ko sadza da aka gubta zai iya canza kashe aiki na ingginzafi kuma taƙawa kansa a kuskure.
Dandalin batteri yana iya taka rawa wajen kawo izinin gini, musamman a kuyun yanar gizo. Batterin da ke karanci ko ba ta samu sauri ba ba za ta iya bawa matakan da ke bukata don kawo girma zuwa ga alkarfi. Tabbatar da testa da tallafin batteri, kamar dade warfannin da duba darajar elektarolaiti, zai taimaka wajen kare wa izinin gini. Sai dai, duba motar starter, tsarin charge na alternator, da haɗin elektrik zai tabbatawa cewa an samu alkarfi a lokacin farawa.
Karkaran tsarin shiga kwantar zai iya karewa kan amfani da injin. Filtarin kwantar da ke rure yana karewa kan shiga kwantar, kuma yana canza tsarin kwantan-ƙwallon da ke bukata don kuskuren. Dubawa da nuniwar filtarin kwantar bisa ma'adinin mai amfani zai tabbatawa cewa injin yana alhaji daidai kuma yana karewa kan karancin wurin abubuwan da ke j внутри.
Abubuwan da ya kamata suyi ne a Iyakokin Injin
Idan kuguran perkins ɗin ka tafi dake da masallaci kamar yadda ya kamata, kamaƙa mai zurfi, canjin ukuwa ko fitar da abuɓin gurji, sai kuma ake buƙatar amfani da rarrabon fahimta. Gurji mai zurfi yana nuna waɗanda ba suka shan kamaƙa saboda kamaƙa wura, filtar hangen bauta ko matsalolin injiktaran. Gurji mai zurfi na blue yana nuna waɗanda ke samun kamaƙa, wato zai halarta ne daga ringolin piston da aka ƙare, cin kashe cylinder ko matsalolin sigar valve, wanda ke richi tallafin malamari.
Gurji mai zurfi a lokacin farawa yana da kyau a lokacin sanyi amma gurji mai zurfi mai zuwa shine nuna waɗanda ke fitowa cikin ruwan kamaƙa, wanda yana nuna waɗanda ke da matsala akan head gasket ko cylinder head mai zurfi. Wadannan matsalolin mahimmanci ke richi tallafin malamari da kimiyya immediate don hana damage mai zurfi akan mesin.
Iya koma dake waje na kayan uku na wuya tare da matsalolin nazarin abubuwa. Kayan amfani masu zurfi ko masu karfi iya haifar da amfani a tsakanin kewayon abubuwa, wanda ya haifar da halayen kuma kama da kama da kwanciyar hankali. Tsawon nazarin kayan abinci da sauraron injin suna taimakawa wajen koyo kwanciyar aiki da kwayoyin abubuwa.
Gwagwado na Nukarin Karkara
Matsalar Samun Kudaden Nukarin Karkara
Matsalolin samun nukarin karkara a cikin ganyunan diesel suna nuna su kamar yadda suna canzawa, alamu ba tare da rashin stabiliti ko kuma farko mai zurfi. Dole ne setar generatarin perkins mai aiki kyauta ya koyo stabilitin voltage da frequency na samawa a kan yanayin load. Lokacin da samun voltage ya fara daga cikin ma'auni masu hanyar, nazarin auta mai nuna voltage (AVR) na buƙatar gyara ko na tsayarwa.
Tabbasin da ma'anar yawa suna nuna batun tsarin kula da kama'irin injin. Tsarin governor ya matsue mataftafin RPM na injin don samar da ma'anar karkashin karkashin kuɗi. Kuskuren tsarin mechanical ko electronic governor zasusun taro da ma'anar yawa wanda zasusun karni sama da abubuwan karkashi. Matsayin tsarin governor da kuma gyara gano waɗannan batuna masu karancewa.
Kama'irin kuɗi duka sai bayan injin ke ayeta normal suna nuna batun alternator ko kama'irin tsarin iskarwa. Duba haɗin alternator, brushes, da rings na slip ta taimaka wajen ganin kuskuren elektrik mai amfani. Karfin kwatanta windings na alternator da tsarin iskarwa yana bukatar shigarwa ga kuskuren elektrik mai tsoro.
Kuskuren Tsarin Kontin
Tsarin kula da suƙurwa na zaman lafiya sun hada da alamar zuwa da kuma ayyukan kula da zauna wanda taushe tsaro da rashin tafiyya. Amma, iri irin kuskuren cibiyar kula zai iya waske tashin sakamakon generator ko ba da shirye-shiryen masifa. Fahimtar ilimin ilmin tsarin kula yana taimakawa wajen fagowa bayan masifa mai kyau da kuskuren tsarin kula.
Nunan cibiyar kula wanda ya nuna lambar kuskure ko saƙon masifa suna buƙatar sharhi mai zurfi bisa dokumentin masu amfani. Kullum lamba na kuskure tana dace da ma'anannin musamman ko ayyukan kula da zaune wanda aka girma don kula da aikace-aikacen. Kuɗiwa da wannan saƙon zai iya haifar da kuskuren mai zurfi ko kuskuren elektrik.
Kamar wani kuskuretsa na sensor daga cikin nuni mai lafiya ya iya haifar da alarma mai sauƙi ko kuma kasa yin aiki ga ayoyin kansa. Iyakar gyara da tabbatar da sa hannun ruwa, sakamako mai tsawon gini, da alamar girma suna taimakawa wajen tabbatar da inganci na bin godiya da kuma aiki mai amintacce na nuni mai lafiya.
Gudanarwa da Kwatanta na Nuni Mai Tsafi
Zukar Tsafi da Masallaci na Saye
Zukar tsafi ta bambanta tasiri akan aiki da zurfin kwana na wani janareta na Perkins . Zukar diesel ta kasance sabada lokaci, musamman lokacin da aka magana shi a matsayin karatun lokaci ba tare da ma'ajinida daya ba. Sayen ruwa ita ce mafi mahimmancin masallaci na nuni mai tsafi, ta haifar da ragewar juyawa da kuma ta yi nasarar inji ta hanyar zingirfa da kuma saye.
Yin amfani da samfurin wuya da kiyasin yunwa ya taimaka wajen nuna alaƙaƙun wurin na yunwa kafin ta shirya matsalolin aikin. Iyakar dubu zai iya nuna alaƙaƙun wuya kamar rarraba ruwa ko kayan dumi, amma kiyasin makaranta yana ba da bayanin kama ga ma'anin yunwa kamar lambobin cetane, abun hankali, da yadda take yanke alaƙaƙun juyawa.
Yin amfani da rashin yunwa na yin amfani da yunwa zai iya kare wasu matsalolin alaƙaƙun wurin. Wannan yana hada da amfani da kayan haɓakke na yunwa, kiyaye takalmomi masu safa, da kafa tsarin canzawa na yunwa don kare matsalolin cinyawa mai tsawo. Kiyaye saukunan takalma da samun ruwa sun kiyaye inganci na tsarin yunwa kuma kare gyara injina suka fi kari.
Kayan Aiki na Tsarin Basiyun Yunwa
Nau'in shiga na kwallon gudu yana ƙarfafa manyan abubuwa da dole su aiki tare da wuyar bawa na kwallon gudu mai zurfi zuwa cikin nazarin shiga. Babban kwallon gudu, faltarai, da ukuwa suna bukatar idofo da sauraro don tabbatar da sauyin kwallon gudu a duk wadansu halayen aiki. Faltarai masu doki suna kiyaye zama na kwallon gudu kuma za suha farawa kwana inganci ko kashe kwallon gudu a lokacin aiki masu girma.
Kama'ilin inji na karamar wuya ya bambanta ainihin aiki na injin, kamar yadda ya riga ke tsawon lokacin da ke tafiyya. Ananƙiya masu ingin karamar wuya suna buƙata tabbatar da inganci da abubuwan da ke juyawa, yayin da masu ingin karamar wuya elektrik suka buƙata tabbatar da haɗin elektrik da gwadawa kan idatti. Idassar karamar wuya ba tare da kyau zai iya shirya batun halartar wuya kuma samun ukuwa.
Daidaitaccen kuyi na kwayoyin wuya yana da mahimmanci wajen kiyaye tsarin tsari kuma taka bauta mai zuwa. Kwayoyin wuya mara bada ko mara tsaka suna ba da damar bauta zuwa cikin tsari, yayin amfani da rashin kai uku kuma zama ayyukan injin. Tattaunawar kwayoyin wuya da haɗuwa ta hanyar nuna yana taimakawa wajen gano masalolin da za su faru kafin su zama abin halartar ayyuka.
Gudanmawa na Tsarin Taguwa
Gyarawa da Hanyar Ruwan Fasaha
Tattara tsarin taguwa ta yadda dole ke yau da mahimmanci wajen kula da kumfa kuma kiyaye ingini na Perkins Generator Set a matsayin karatu. Tsarin taguwa yana cire kumfa wanda yaƙi bayan karni, kuma yana kiyaye girman ƙima mai kyau a karkashin yanayin bebe ne. Yanke yanke na girman coolant da gwadawa tsarin tsari ta hanyar tsari yana taimakawa wajen gano daki ko rashin aiki na kayan ajiyar kafin su zama abin halartar injin.
Yiwa mai tsada yana tafarka tsarin aiki da ingancin abubuwan. Amfani da sauya mai kyau na yiwa mai tsada yana ba da tsaro don kula, tsaro don zama mai korosi, da kuma iyaka mai amfani da hankali. Tambayoyin yanayi na yiwa mai tsada suna nuna girman wuta da rashin kayan additivu, wanda yana nuna lokacin da ake buƙatar canza yiwa mai tsada. Kuɓiye aiki na yiwa mai tsada zai iya haɗawa da shirabe mai tsada, kasaƙo mai dawo, da kuma zama mai korosi a cikin mesin.
Aiki na thermostat yana iya ranar mahimmanci wajen koyo tsarin mesin zuwa ma'adin girmama. Zama mai sauƙi na thermostat zai iya haɗawa da kula ko kuma kula da koyo mesin zuwa ma'adin girmama mai amfani, wanda zai tafiya tsinkin kwayoyin kwayo da zarar. Tambayoyin alamu na thermostat da kuma canje wannan saboda takwara ta aiki taya kula da masallaci.
Masallaci na Heat Exchanger da Radiator
Alamuƙan yawan zuma da alamuƙan yawa suna canza zuma daga coolant ta hanyar tsarin baki da ma'adinin yawa. Yawan alamuƙan yawa ko kewayon alamuƙan yawa suna nake sauya tasowa da bisa sa guduwa a lokacin yawan gudu ko a lokacin amfani da wani abu ne mai sauƙi. Gwadawa daya daya na alamuƙan yawa da alamuƙan yawa na radiator suna taimakawa wajen samun tasowar ma'adinin yawa.
Aiki na fana ita ce babban mahimmacin samar da baki mai zurfi a cikin tsarin gwada. Alamuƙan fana da ke amfani da belts suna buƙatar gwada daya daya da sauya, yayin da electric cooling fans suna buƙatar gwadawa a cikin haɗin elektric da gwada mota. Baki mara zurfi za ta iya sabunta satsunan ruwa wanda ba za ta shiga alarma amma ta kama karancin cin gudummawa.
Kunya tsarin coolant bisa ta shawe da taka tsanyawa a wani yanar gizo ko kuma karin karbar abubuwa. Kunya scale a cikin radiators, tsarin clogged a cikin engine block, ko kuma water pumps suka fara rinka yana nufin zama ba za a iya tsayar da coolant. Tsarin majogo da kuma gwadawa yana taduwar matsalolin circulation kafin su zama abin da ya sauke.
Gwadawa tsarin lubrication
Gwadawa uku da kyau na zarar
Tsarin lubrication keba da amintamai mahaifan abubuwan ingjin mai dokin a cikin perkins generator set. Gwadawa uku na zarar ke taimakawa wajen warware matsaloli kamar fafatacciyar pompu, burrun bantalan, ko nufofin zarar da zai iya haifar da karin karbar ingjin. Gwadawa uku na zarar akan yau da kullun a kuyun halayyin aiki ke tabbatar da sauya mai zurfi a kowane yanar ingjin da ma'anar load.
Tattaunawar kayan tsanyi ta bamuƙa bayani mai tsada game da halin injin da kwayoyin nufin nazarin kayan tsanyi. Dandalin iri ne na kayan tsanyi suna nuna kayan sassa, yayin da kayan tsanyin wuya yana nuna rashin taimakewa ko masallaci na waƙaƙe. Tattara da tattaunawa kayan tsanyi a karkashin lokaci ta bambuɗawa masallacin da ba za su kasance shirye-shiryen duniya domin samun karanciwa mai kyauta.
Gudanwarsa tsanyin kayan tsanyi ita ce abin dake tsakiyar iko ingin injin. Tsanyin kayan tsanyi mai gini zai haifar da alamar nufi da kuma sauyin kayan sassa, yayin da ƙayyade kayan tsanyi zai haifar da girman idodi na kayan tsanyi da kuma rashin taimakewa. Gudanwar kayan tsanyi a karkashin lokaci da sauya kayan tsanyi a lokacin da aka fada shi zai kiyaye iyaka mai zurfi na nazarin nufin kayan tsanyi.
Gudanwar Kayan Iko na Tsanyin Kayan Tsanyi
Filtarar zarafi suna iya matuƙin mahimmacin ingantacciyar zarafi ta hanyar kawo abubuwan da suka shakata. Filtarar zarafi masu gurji zai iya haifar da karaɓar pressure na zarafi da aikin sabon filtar, zai ba da damar zarafin da ba a filta ba ya tsayi wajen tafiyya a cikin injin. Sabuntawa daya daga biyu na filtar yayin da aka nuna wa'adadi zai iya tabbatar da ingantacciyar abubuwan da suka shakata da kuma yin kara mataimakin injin.
Kwamfutar zarafi dole ne su yi inganta pressure da flow a duka samun rashin karfin kwamfuta. Karin amfani kwamfutar zai iya haifar da karamin pressure wacce bai iya haifar da alamu ba amma ta kare mataimakinta. Ayyukan gwaji da sabunta kwamfuta zarafi a lokacin da ake bukata zai iya kula da kariyar mataimaki da sauya injin
Tsarin karkashin crankcase ya na'ura tsakanin damar gafara wanda zai haifar da matsalolin rufe shine ayyukan ruwa da rashin runtse. Zama'in tsarin breathers za su haifar da ƙarin pressure a cikin crankcase, wanda zai haifar da amfani da zurfi da rashin sauƙin yawa. Nawayin nasa da sakawa na regular breather suna taimakawa wajen samun pressure mai kyau a cikin crankcase kuma suna kara shan zurfi.
Tambayoyi Masu Yawan Faruwa
Wane ne duniyoyin da ke yiwuwa a hanyar farawa ta generator set na perkins
Duniyoyin da ke faruwa masu farawa su ne: battery marna ko mai karfi, koro mai zurfi, filtar zuwa mai gafara, tangi mai zurfi, starter motor mara aiki. Matsalolin battery suna taka muhimmiyar burin (60%) daga karkashin matsalolin farawa, musamman a lokacin sanyi. Yi la'akari da duba girma voltage na battery da specific gravity baya kawo sauya akan dubawa wadansu duniya biyu. Matsalolin zuwa kamar yadda yana ɗaukata da ruwa, kafa, ko diesel mai karfi zai iya kirkiro azumi da farawa.
Mene ne kadan lokaci in buƙe yi maintenance a generator din diesel
Ƙimar yin amfani da waje da shirye-shiryen duniya suna tsawon karfin kiyaye, amma zabba’i masu damar yin lafiya na kwanaki, gwaji na uku, gwajin zarafi na wata, da kuma sauraron kwana. Anoƙin canja zararin injin zai kasance kusan kowane 250-500 ayyuka, yayin da zararen abubuwa na kowane 500-1000 ayyuka. Zararen hawa za su buƙatar dubawa kowane 100 ayyuka kuma canja bisa halayensu. Ku yi amfani da shawarwari na mai tsara don sigar ku da halayen yin amfani.
Me ya kamata injin ku ta produce voltage mara daidaita
Zaune mai yawa tauna ne a matsayin saboda matsalolin mai tsawon voltage, matsalolin alternator ko canje-canjen shekara na injin. Mai tsawon voltage ya bada gudunmawar kwamfuta kuma za a bukatar saita shi ko maye shi idan an sami canje-canje mai zurfi. Matsalolin alternator kamar wani abu mai dadi, tushen da aka daki ko matsalolin haɓakke zai iya sabota canje-canje mai zurfi na voltage. Canje-canjen shekara na injin saboda matsalolin mai ambali ko masalolin nuni na kwayar za ta shiga canje-canje na voltage da frequency wanda zai iya rukowa kayan aikin da aka haɗa.
Mene ne zan yi idan generatormi ya zuba bayan aiki
Ana buƙatar rage waƙa'asauyi zarar da aka kula da rashin kula da tsarin, domin dawo da rashin kula da injin. Bayan kula da injin yana dare, dubi girman coolant, dubi don kwafin, da tabbata tsarin aiki na fan. Zabinku masu damar haɗuwa, masu kuskuretsin thermostat ko wani batutuwan tushen ruwa suna dabba tambayoyin kula da su. Karatu kwafi matakan radiator bayan system ya zama mai zurfi, saboda ruwan coolant tare da pressure zai iya haɓaka alawa. Harkar ilimi ana buƙaci wannan yana iya nuna rashin shirye-shiryen injin kamar nau'in matarci na head gasket ko alakarruwa masu kuskuren coolant wanda ke kawo zuwa kula da iyaka.

